Immunohistochemical and Morphopathological Features of Multiple Cutaneous Mast Cell Tumor in a Cow
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.24070/bjvp.1983-0246.008014Keywords:
multiple mast cell tumor, pathology, immunohistochemistry, cattleAbstract
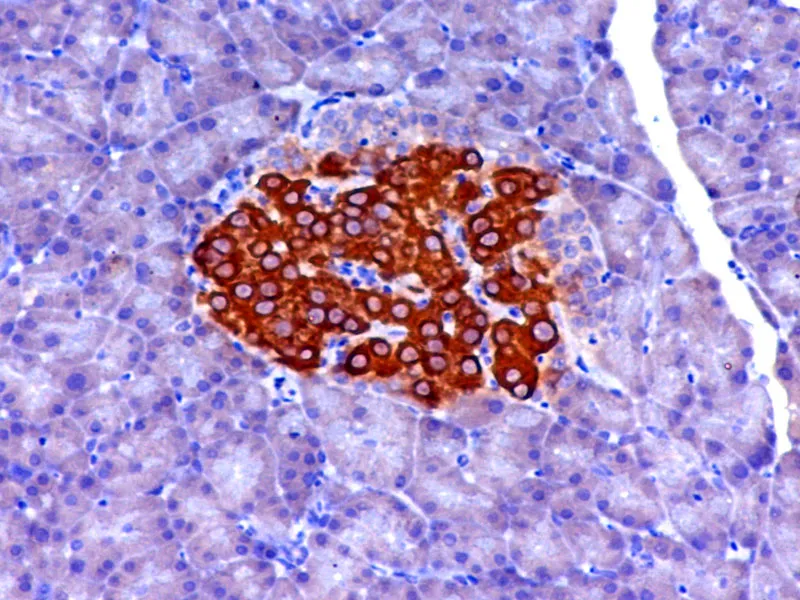
A 4 year old female Holstein cow with multiple skin lesions was referred for clinical examination. Grossly, approximately 60 discrete cutaneous nodules and masses with variable sizes ranging from 1 to 5 cm were observed on both sides of flunks, shoulders, neck, back, and mammary glands. Histopathologically, the masses were composed of non-encapsulated accumulation of neoplastic round cells contained moderate to abundant amounts of finely eosinophilic granules in the cytoplasm. Cellular or nuclear pleomorphism and mitotic figures were not remarkable. Metachromasia was seen in cytoplasmic granules stained with toluidine blue. In the immunohistochemical staining, the neoplastic cells were positive for vimentin and c-kit. No immunoreactivity was seen for cytokeratin and HMB - 45. Based on these findings, multiple cutaneous mast cell tumor was diagnosed. Immunohistochemical features of mast cell tumor have not been reported previously in cattle.