Hepatogenous chronic copper toxicosis associated with grazing Brachiaria decumbens in a goat
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.24070/bjvp.1983-0246.009019Keywords:
diseases of goats, liver diseases, toxicosis, copper, poisonous plantsAbstract
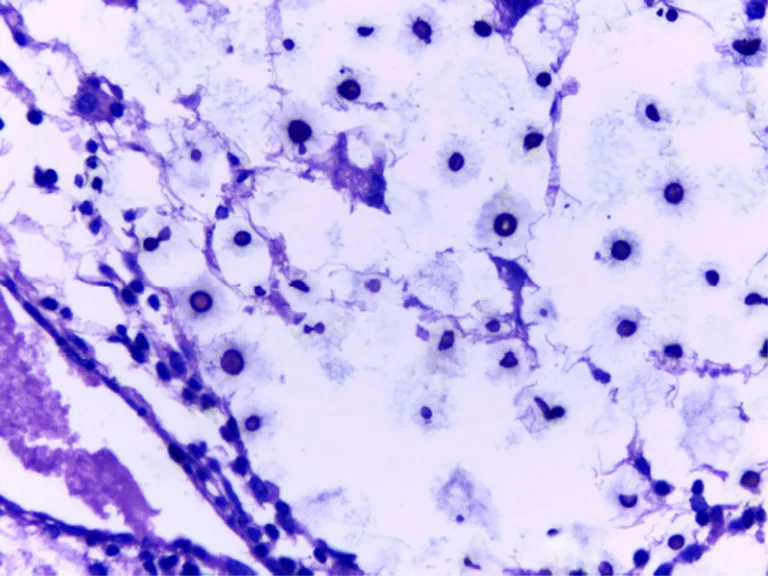
A case of hepatogenous chronic copper toxicosis associated with ingestion of Brachiaria decumbens in a 4-year-old female is reported in a goat from a herd of approximately 1,000 goats of different categories, all grazing in a pasture consisting exclusively of B. decumbens. The goat had chronic weight loss, dehydration, and apathy. Just prior to death it developed anemia, icterus and hemoglobinuria. Necropsy findings included marked icterus, enhanced lobular pattern and orange discoloration of the liver, pulmonary edema, distention of the gall bladder and hemoblobinuric nephrosis. Histopathological examination of the liver revealed marked random degeneration and necrosis of individual hepatocytes, marked bilestasis, intracytoplasmic hemosiderin in hepatocytes and Kupffer cells, birefringent crystals with bile staining in the lumen of bile ducts, and sparse, randomly distributed foamy macrophages. Severe multifocal tubular degeneration and necrosis associated with multiple hyaline and coarsely granular hemoglobin casts were observed in the kidneys. Copper levels determined in liver and kidney samples by atomic absorption spectrophotometry were 410 ppm of liver dry matter and 34.4 ppm (kidney, dry matter). The gross, histopathological findings and copper analysis in the tissues of this goat led to a final diagnosis of hepatogenous chronic copper toxicosis associated with grazing of B. decumbens.