In vitro and in vivo antiparasitic action of essential oils of Lippia spp. in Koi Carp (Cyprinus carpio) fed supplemented diets
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.24070/bjvp.1983-0246.v12i3p88-100Keywords:
fish farming, phytotherapics, efficacy, ectoparasitesAbstract
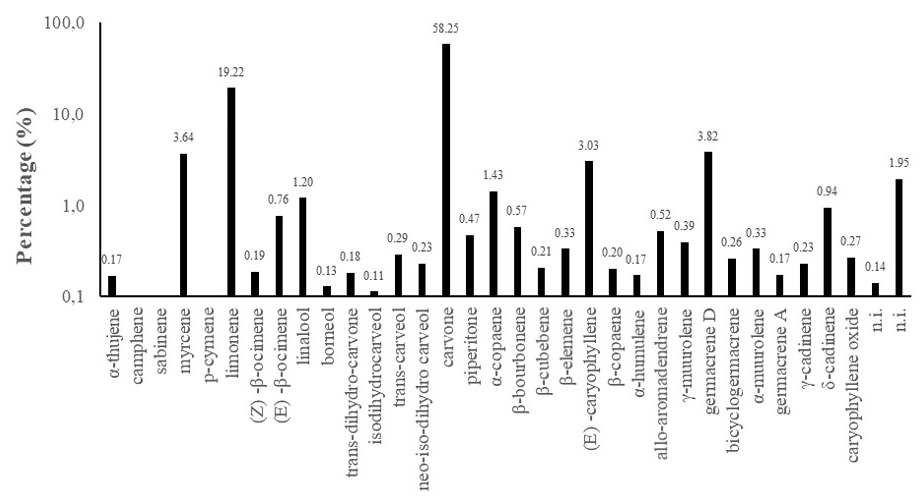
This study evaluated the in vitro antiparasitic activity of the essential oils of Lippia alba, L. origanoides and L. sidoides against monogenean parasites of koi carp Cyprinus carpio and its zootechnical performance in net cages. The oils were obtained from the leaves by hydro distillation, and the chemical composition was evaluated via gas chromatography. In vitro assays were performed with each essential oil separately and combined in binary (1:1) and tertiary (1:1:1) mixtures with the Lippia species at 10, 20, 40, 60, 80 and 100 mg L-1 and two control groups (grain alcohol and tank water). To determine zootechnical performance, L. sidoides oil was added to the feed at 0.00 (control), 0.25, 0.50, 0.75 and 1%, in triplicate and with 20 fish per net cage fed for 60 days. The best results in vitro against monogeneans were observed for L. sidoides (40 mg L-1 in 8 min), followed by L. origanoides (40 mg L-1 in 25 min) and L. alba (40 mg L-1 in 4 h). Reductions in weight gain, protein efficiency rate and specific growth rate were observed in diets containing 0.75% of L. sidoides oil in comparison to the control and the 0.25% diet. There were no significant differences in growth, individual mean feed intake, apparent feed conversion and parasitological indices. Based on our results, 0.25% L. sidoides oil showed the best zootechnical performance, but was not effective against koi carp parasites in vivo.