Characterization of macrophage polarization in lesions of dogs inoculated with Leishmania (Leishmania) infantum (BH401) strain
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.24070/bjvp.1983-0246.v15i1p11-19Keywords:
Visceral leishmaniasis, pathologic anatomy, L. infantum, macrophages, TGF-β1, CD163, Calprotectin (L1)Abstract
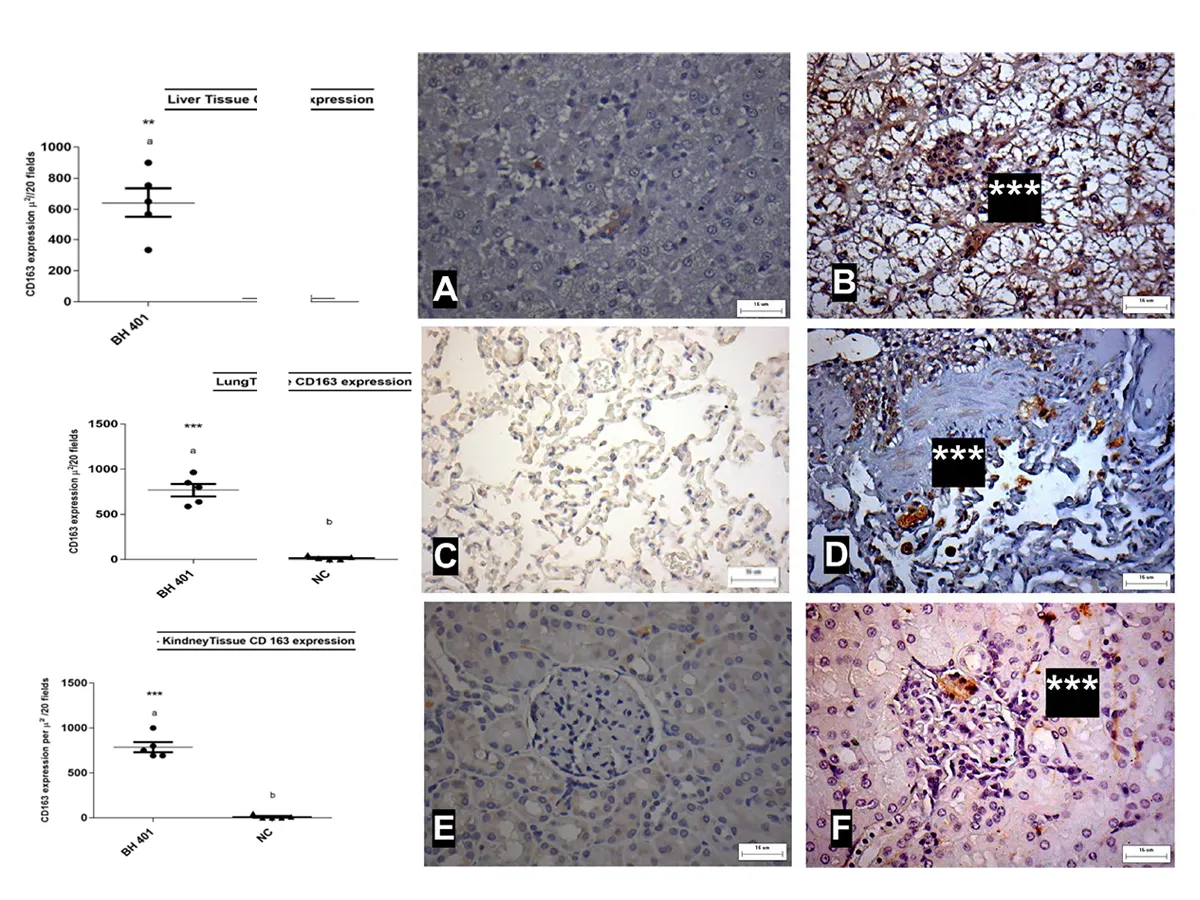
The aim of this work was to describe the anatomical pathology of dogs experimentally infected with Leishmania (Leishmania) infantum strain MCAN / BR / 2002 / BH401, a Brazilian form of L. infantum isolated from a symptomatic dog from an endemic area. For this, five beagles (three months old and both sexes) composed the experimental group. Markers of macrophage subpopulations M1 and M2 (related to resistance and susceptibility to visceral leishmaniasis) and the tissue cytokine transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1) (one of the main cytokines related to the fibrosis process and anti-inflammatory action) were evaluated in livers, lungs and kidneys. The BH 401 L. infantum strain induced classical lesions of the visceral disease where all evaluated organs showed a chronic inflammatory reaction and tissue parasitism associated with a higher expression of CD163 and TGF-β1 markers, might be related to the progression of the disease. In this work it was possible to conclude that the BH 401 strain reproduces canine visceral leishmaniasis that occurs naturally.