Clinicopathological and immunohistochemical features of insulinoma in an adult mixed breed dog
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.24070/bjvp.1983-0246.v16i3p188-191Keywords:
insulinoma, canine, hypoglycemia, metastasis, pancreasAbstract
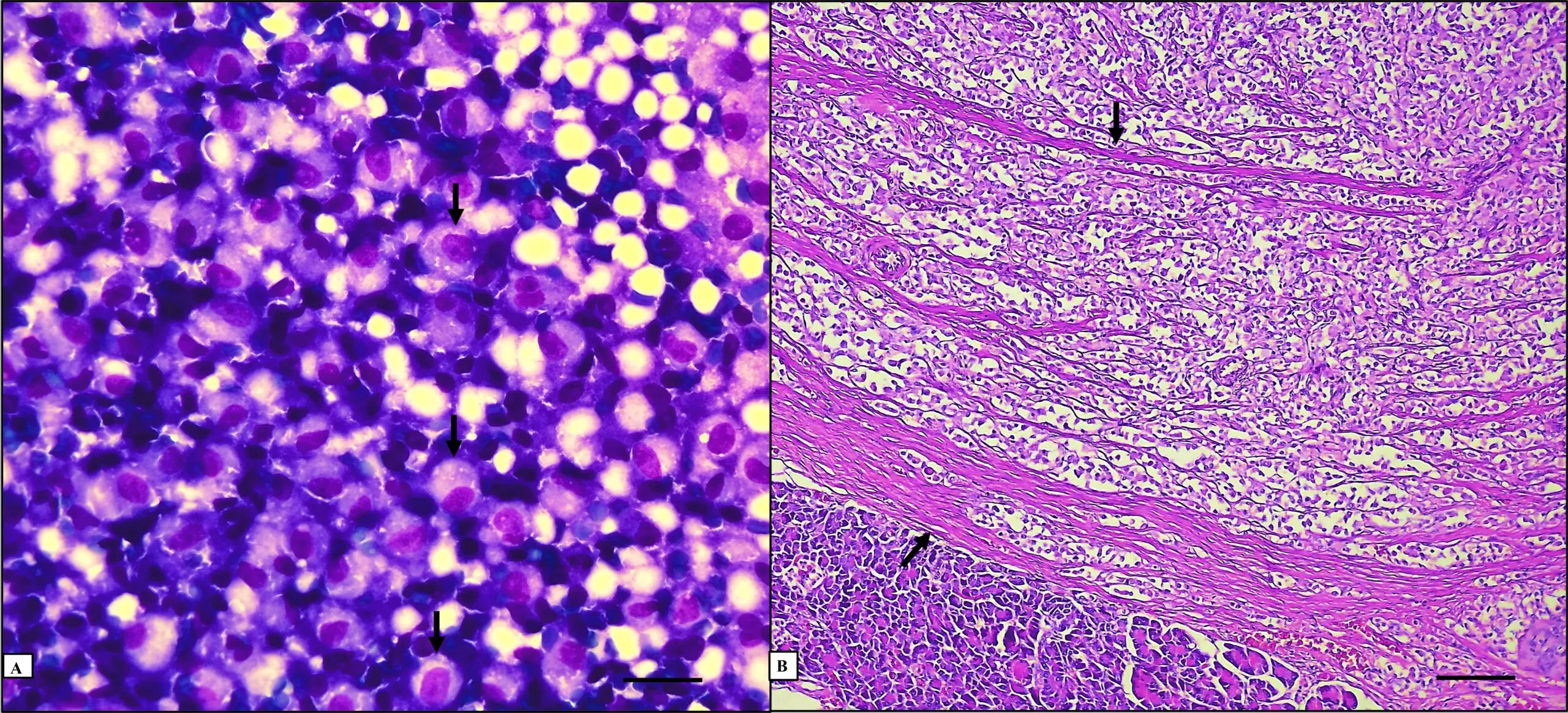
Canine insulinoma is a common non-specific neoplasm with high metastasizing ability. Its epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment are well described. However, its long-term prognosis is considered poor. We report a rare case of insulinoma in a small-size, mixed-breed adult dog, which presented with a circling walk, seizures, weakness, depressed mental state, and hypoglycemia. Glucose continuous rate infusion, diazepam, and phenobarbital were initiated to stabilize the glycemia and control the convulsion. Blood tests, fine needle aspiration cytology, ultrasound and radiological tests, and histology and immunohistochemical analysis confirmed the diagnosis of insulinoma, emphasizing the relevance of considering it as a differential diagnosis for small canine breeds and younger animals. Further, dogs can be regarded as an experimental animal model for human insulinoma research as they share characteristics.